点击(此处)折叠或打开
-
https://www.cnblogs.com/ginvip/p/6352157.html
-
AWK 为三位创始人的缩写.
-
AWK 程序设计语言, 定义为“样式扫描和处理语言”。它允许您创建简短的程序,这些程序读取输入文件、为数据排序、处理数据、对输入执行计算以及生成报表,还有无数其他的功能。
-
-
awk 是一种很棒的语言,它适合文本处理和报表生成,其语法较为常见,借鉴了某些语言的一些精华,如 C 语言等。
-
-
使用方法
-
awk '{pattern + action}' {filenames}
-
-
pattern 表示 AWK 在数据中查找的内容,pattern就是要表示的正则表达式,用斜杠括起来。
-
action 是在找到匹配内容时所执行的一系列命令。
-
{}不需要在程序中始终出现,但它们用于根据特定的模式对一系列指令进行分组。
-
花括号用于将几块代码组合到一起
-
-
awk语言的最基本功能是在文件或者字符串中基于指定规则浏览和抽取信息,awk抽取信息后,才能进行其他文本操作。完整的awk脚本通常用来格式化文本文件中的信息。
-
- 通常,awk是以文件的一行为处理单位的。awk每接收文件的一行,然后执行相应的命令,来处理文本。
点击(此处)折叠或打开
- # awk -F":" '{print $0}' /etc/passwd
-
 $0 为一整行 root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
$0 为一整行 root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
- $1 为 root $2为x FS:字段分隔符 NF为字段数量 NR 为记录(行数)的数量.
-
-F参数:指定分隔符,可指定一个或多个


点击(此处)折叠或打开
-
# awk '{if(NR>=20 && NR<=30) print $1}' test.txt
-
-
只查看test.txt文件(100行)内第20到第30行的内容
-
-
-
# awk -F '[ ,]+' '{print $3" "$7}' test.txt
- 设定多个分隔符, 然后打印 并以空格分隔.
点击(此处)折叠或打开
-
BEGIN 和 END 模块
-
-
对于每个输入行, awk 都会执行每个脚本代码块一次
-
awk 在开始处理输入文件之前会执行 BEGIN 块,因此它是初始化 FS(字段分隔符)变量、打印页眉或初始化其它在程序中以后会引用的全局变量的极佳位置。
-
- awk 在处理了输入文件中的所有行之后执行 END块, END 块用于执行最终计算或打印应该出现在输出流结尾的摘要信息。
-
- # awk 'BEGIN {count=0;print "[start] user count is ",count} {count=count+1;print $0} END{print "[end] user count is ",count}' passwd
- 统计/etc/passwd的账户人数, count 为自定义变量.
-
- # ll |awk 'BEGIN {size=0;} {size=size+$5;} END{print "[end]size is ",size}'
-
统计某个文件夹下的文件占用的字节数
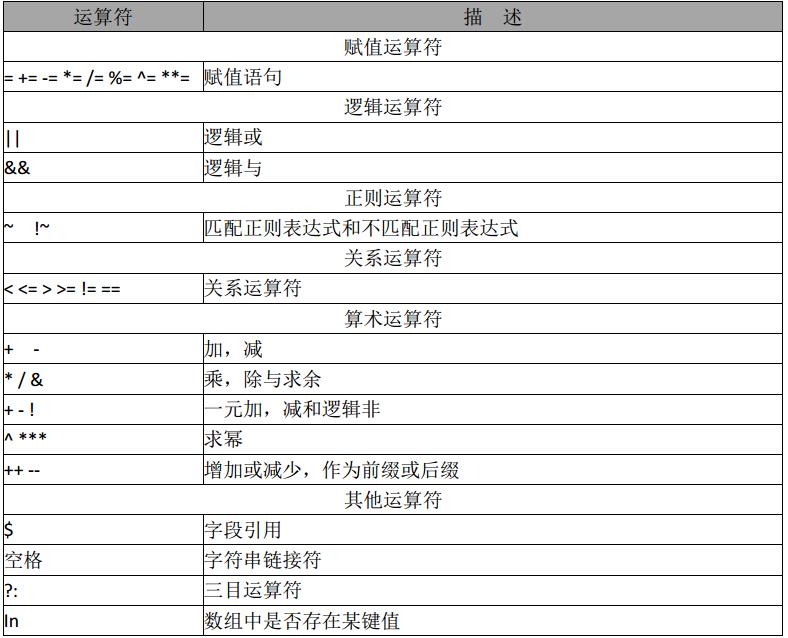

点击(此处)折叠或打开
-
awk 赋值运算符:a+5;等价于: a=a+5;其他同类
-
# awk 'BEGIN{a=5;a+=5;print a}'
-
-
# awk 'BEGIN{a=1;b=2;print (a>2&&b>1,a=1||b>1)}'
-
awk逻辑运算符, 返回 0 1
-
-
# awk 'BEGIN{a="100testaa";if(a~/100/) {print "ok"}}'
-
返回 ok a变量 ~匹配 包含/100/.
-
# echo|awk 'BEGIN{a="100testaaa"}a~/test/{print "ok"}'
-
返回ok
-
-
-
关系运算符:
-
如: > < 可以作为字符串比较,也可以用作数值比较,关键看操作数如果是字符串就会转换为字符串比较。两个都为数字 才转为数值比较。字符串比较:按照ascii码顺序比较。
-
-
awk 算术运算符:
-
说明,所有用作算术运算符进行操作,操作数自动转为数值,所有非数值都变为0。
-
-
-
三目运算符 ?:
-
# awk 'BEGIN{a="b";print a=="b"?"ok":"err"}'
-
ok

点击(此处)折叠或打开
-
awk 赋值运算符:a+5;等价于: a=a+5;其他同类
-
# awk 'BEGIN{a=5;a+=5;print a}'
-
-
# awk 'BEGIN{a=1;b=2;print (a>2&&b>1,a=1||b>1)}'
-
awk逻辑运算符, 返回 0 1
-
-
# awk 'BEGIN{a="100testaa";if(a~/100/) {print "ok"}}'
-
返回 ok a变量 ~匹配 包含/100/.
-
# echo|awk 'BEGIN{a="100testaaa"}a~/test/{print "ok"}'
-
返回ok
-
-
-
关系运算符:
-
如: > < 可以作为字符串比较,也可以用作数值比较,关键看操作数如果是字符串就会转换为字符串比较。两个都为数字 才转为数值比较。字符串比较:按照ascii码顺序比较。
-
-
awk 算术运算符:
-
说明,所有用作算术运算符进行操作,操作数自动转为数值,所有非数值都变为0。
-
-
-
三目运算符 ?:
-
# awk 'BEGIN{a="b";print a=="b"?"ok":"err"}'
- ok
点击(此处)折叠或打开
-
字段分隔符 FS
-
FS="\t" 一个或多个 Tab 分隔
-
-
FS="[[:space:]+]" 一个或多个空白空格, 为默认情况
-
FS="[" ":]+" 以一个或多个空格或:分隔
-
-
-
字段数量 NF
-
# awk -F ":" 'NF==8{print $0}' hello.txt
-
-
-
记录数量 NR
-
# ifconfig eth0|awk -F [" ":]+ 'NR==2{print $4}' ## NR==2也就是取第2行
-
-
-
RS 记录分隔符变量.
-
将 FS 设置成"\n"告诉 awk 每个字段都占据一行。通过将 RS 设置成"",还会告诉 awk每个地址记录都由空白行分隔
-
-
-
[root@Gin scripts]# cat recode.txt
-
Jimmy the Weasel
-
100 Pleasant Drive
-
San Francisco,CA 123456
-
-
Big Tony
-
200 Incognito Ave.
-
Suburbia,WA 64890
-
[root@Gin scripts]# cat awk.txt ## 代码块
-
#!/bin/awk
-
BEGIN {
-
FS="\n"
-
RS=""
-
}
-
{
-
print $1","$2","$3
-
}
-
[root@Gin scripts]# awk -f awk.txt recode.txt
-
Jimmy the Weasel,100 Pleasant Drive,San Francisco,CA 123456
-
Big Tony,200 Incognito Ave.,Suburbia,WA 64890
-
-
-
OFS 输出字段分隔符
-
[root@Gin scripts]# cat hello.txt
-
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
-
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin:888
-
[root@Gin scripts]# awk 'BEGIN{FS=":"}{print $1","$2","$3}' hello.txt
-
root,x,0
-
bin,x,1
-
[root@Gin scripts]# awk 'BEGIN{FS=":";OFS="#"}{print $1,$2,$3}' hello.txt
-
root#x#0
-
bin#x#1
-
-
-
ORS 输出记录分隔符
-
[root@Gin scripts]# cat recode.txt
-
Jimmy the Weasel
-
100 Pleasant Drive
-
San Francisco,CA 123456
-
-
Big Tony
-
200 Incognito Ave.
-
Suburbia,WA 64890
-
[root@Gin scripts]# cat awk.txt
-
#!/bin/awk
-
BEGIN {
-
FS="\n"
-
RS=""
-
ORS="\n\n"
-
}
-
{
-
print $1","$2","$3
-
}
-
[root@Gin scripts]# awk -f awk.txt recode.txt
-
Jimmy the Weasel,100 Pleasant Drive,San Francisco,CA 123456
-
- Big Tony,200 Incognito Ave.,Suburbia,WA 64890

点击(此处)折叠或打开
-
正则应用
-
规则表达式
-
-
awk '/REG/{action} ' file
-
-
/REG/为正则表达式,可以将$0 中,满足条件的记录送入到:action 进行处理
-
-
# awk '/root/{print $0}' passwd ##匹配所有包含root的行
-
-
# awk -F: '$5~/root/{print $0}' passwd ## 以分号作为分隔符,匹配第5个字段是root的行
-
-
# ifconfig eth0|awk 'BEGIN{FS="[[:space:]:]+"} NR==2{print $4}'
-
-
-
-
布尔表达式
-
awk '布尔表达式{action}' file 仅当对前面的布尔表达式求值为真时, awk 才执行代码块。
-
# awk -F: '($1=="root")&&($5=="root") {print $0}' passwd
-
-
awk 的 if、循环和数组
-
-
{
-
if ($1=="foo"){
-
if($2=="foo"){
-
print "uno"
-
}else{
-
print "one"
-
}
-
}elseif($1=="bar"){
-
print "two"
-
}else{
-
print "three"
-
}
-
}
-
-
-
同样的 ! /matchme/ { print $1 $3 $4 } 可以转换为
-
{
-
if ( $0 !~ /matchme/ ) {
-
print $1 $3 $4
-
}
-
}
-
-
-
循环结构 do while.
-
-
{
-
count=1
-
do {
-
print "I get printed at least once no matter what"
-
} while ( count !=1 )
-
}
-
-
-
for 循环
-
for ( initial assignment; comparison; increment ) {
-
code block
-
}
-
例如
-
for ( x=1;x<=4;x++ ) {
-
print "iteration", x
-
}
-
-
-
-
break 和 continue
-
#break 语句示例
-
x=1
-
while(1) {
-
print "iteration", x
-
if ( x==10 ) {
-
break
-
}
-
x++
-
}
-
-
x=1
-
while (1) {
-
if ( x==4 ) {
-
x++
-
continue
-
}
-
print "iteration", x
-
if ( x>20 ) {
-
break
-
}
-
x++
-
}
-
-
-
数组
-
AWK 中的数组都是关联数组,数字索引也会转变为字符串索引
-
-
{
-
cities[1]=”beijing”
-
cities[2]=”shanghai”
-
cities[“three”]=”guangzhou”
-
for( c in cities) {
-
print cities[c]
-
}
-
print cities[1]
-
print cities[“1”]
-
print cities[“three”]
-
}
-
for…in 输出,因为数组是关联数组,默认是无序的。所以通过 for…in 得到是无序的数组
-
-
-
数组的典型应用
-
用 awk 中查看服务器连接状态并汇总
-
netstat -an|awk '/^tcp/{++s[$NF]}END{for(a in s)print a,s[a]}'
-
ESTABLISHED 1
-
LISTEN 20
-
-
或者
-
awk '{a[$7]+=$10;++b[$7];total+=$10}END{for(x in a)print b[x],x,a[x]|"sort -rn -k1";print
-
"total size is :"total}' /app/log/access_log
-
total size is :172230
-
21 /icons/poweredby.png 83076
-
14 / 70546
-
8 /icons/apache_pb.gif 18608
-
a[$7]+=$10 表示以第 7 列为下标的数组( $10 列为$7 列的大小),把他们大小累加得到
-
$7 每次访问的大小,后面的 for 循环有个取巧的地方, a 和 b 数组的下标相同,所以一
-
条 for 语句足矣


点击(此处)折叠或打开
-
正则应用
-
规则表达式
-
-
awk '/REG/{action} ' file
-
-
/REG/为正则表达式,可以将$0 中,满足条件的记录送入到:action 进行处理
-
-
# awk '/root/{print $0}' passwd ##匹配所有包含root的行
-
-
# awk -F: '$5~/root/{print $0}' passwd ## 以分号作为分隔符,匹配第5个字段是root的行
-
-
# ifconfig eth0|awk 'BEGIN{FS="[[:space:]:]+"} NR==2{print $4}'
-
-
-
-
布尔表达式
-
awk '布尔表达式{action}' file 仅当对前面的布尔表达式求值为真时, awk 才执行代码块。
-
# awk -F: '($1=="root")&&($5=="root") {print $0}' passwd
-
-
awk 的 if、循环和数组
-
-
{
-
if ($1=="foo"){
-
if($2=="foo"){
-
print "uno"
-
}else{
-
print "one"
-
}
-
}elseif($1=="bar"){
-
print "two"
-
}else{
-
print "three"
-
}
-
}
-
-
-
同样的 ! /matchme/ { print $1 $3 $4 } 可以转换为
-
{
-
if ( $0 !~ /matchme/ ) {
-
print $1 $3 $4
-
}
-
}
-
-
-
循环结构 do while.
-
-
{
-
count=1
-
do {
-
print "I get printed at least once no matter what"
-
} while ( count !=1 )
-
}
-
-
-
for 循环
-
for ( initial assignment; comparison; increment ) {
-
code block
-
}
-
例如
-
for ( x=1;x<=4;x++ ) {
-
print "iteration", x
-
}
-
-
-
-
break 和 continue
-
#break 语句示例
-
x=1
-
while(1) {
-
print "iteration", x
-
if ( x==10 ) {
-
break
-
}
-
x++
-
}
-
-
x=1
-
while (1) {
-
if ( x==4 ) {
-
x++
-
continue
-
}
-
print "iteration", x
-
if ( x>20 ) {
-
break
-
}
-
x++
-
}
-
-
-
数组
-
AWK 中的数组都是关联数组,数字索引也会转变为字符串索引
-
-
{
-
cities[1]=”beijing”
-
cities[2]=”shanghai”
-
cities[“three”]=”guangzhou”
-
for( c in cities) {
-
print cities[c]
-
}
-
print cities[1]
-
print cities[“1”]
-
print cities[“three”]
-
}
-
for…in 输出,因为数组是关联数组,默认是无序的。所以通过 for…in 得到是无序的数组
-
-
-
数组的典型应用
-
用 awk 中查看服务器连接状态并汇总
-
netstat -an|awk '/^tcp/{++s[$NF]}END{for(a in s)print a,s[a]}'
-
ESTABLISHED 1
-
LISTEN 20
-
-
或者
-
awk '{a[$7]+=$10;++b[$7];total+=$10}END{for(x in a)print b[x],x,a[x]|"sort -rn -k1";print
-
"total size is :"total}' /app/log/access_log
-
total size is :172230
-
21 /icons/poweredby.png 83076
-
14 / 70546
-
8 /icons/apache_pb.gif 18608
-
a[$7]+=$10 表示以第 7 列为下标的数组( $10 列为$7 列的大小),把他们大小累加得到
-
$7 每次访问的大小,后面的 for 循环有个取巧的地方, a 和 b 数组的下标相同,所以一
- 条 for 语句足矣
点击(此处)折叠或打开
-
替换
-
-
awk 'BEGIN{info="this is a test2010test!";gsub(/[0-9]+/,"!",info);print info}' this is a
-
在 info 中查找满足正则表达式, /[0-9]+/ 用”!”替换,并且替换后的值,赋值给 info 未
-
给 info 值,默认是$0
-
-
查找
-
awk 'BEGIN{info="this is a test2010test!";print index(info,"test")?"ok":"no found";}'
-
ok #未找到,返回 0
-
-
匹配查找
-
awk 'BEGIN{info="this is a test2010test!";print match(info,/[0-9]+/)?"ok":"no found";}'
-
ok #如果查找到数字则匹配成功返回 ok,否则失败,返回未找到
-
-
截取
-
awk 'BEGIN{info="this is a test2010test!";print substr(info,4,10);}'
-
s is a tes #从第 4 个 字符开始,截取 10 个长度字符串
-
-
分割
-
awk 'BEGIN{info="this is a test";split(info,tA," ");print length(tA);for(k in tA){print k,tA[k];}}'
-
4 4 test 1 this 2 is 3 a
- #分割 info,动态创建数组 tA,awk for …in 循环,是一个无序的循环。 并不是从数组下标 1…n 开始